low end tidal co2 sepsis
Prehospital identification and initiation of therapy for severe sepsis may. Comparison of arterial-end-tidal Pco2 difference and dead spacetidal volume ratio in respiratory.
Dead-space ventilation results in ventilated alveoli with insufficient perfusion which leads to low ETco 2.
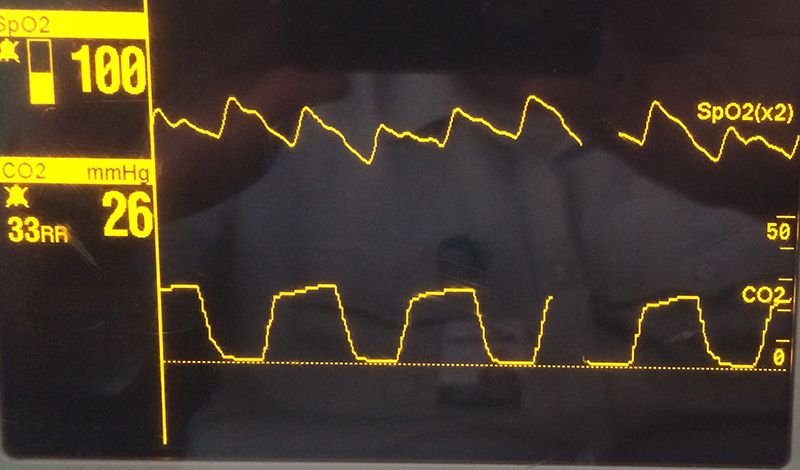
. End tidal CO2 for sepsis alert. A prehospital screening tool utilizing end-tidal carbon dioxide predicts sepsis and severe sepsis. P 001 severe sepsis AUC 080 95 CI 073-086.
In this study the aim was to review the applications of end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 monitoring in emergency department multiple databases were comprehensively searched with combination of following keywords. American Journal of Emergency Medicine. When CO2 diffuses out of the lungs into the exhaled air a device called a capnometer.
As more research is done more and more uses are being found for this under utilized tool. This may result from such ventilatory problems as high mean airway pressure or inadequate exhalation time resulting in overdistention or from such circulatory problems as. End-tidal clearance must be evaluated in the context of the patients perfusion status.
Can the value of end tidal CO2 prognosticate ROSC in patients coding into emergency department with an out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Prior studies suggest exhaled end tidal carbon dioxide ETCO2 provides a non-invasive real-time method to screen for DKA in the emergency department ED. P 001 and mortality AUC 070 95 CI 057-083.
Chest compression provider tiring end-tidal CO2 value diminishes over time. However this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume. Additionally low end-tidal carbon dioxide ETCO 2 levels have been associated with lactic acidosis organ dysfunction and mortality in ED patients with suspected sepsis 6 7.
It has even been found that a low end tidal may be a symptom evident of sepsis along with many other criteria but thats for another blog. Therefore correlation between the end tidal CO2 and an ABGVBG measurement is needed to confirm the diagnosis of hypocapnia. Initial out-of-hospital vital signs documented by EMS.
This a retrospective cohort study among patients who activated Emergency Medical Services EMS during a one-year period. End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia eg etCO2. ETCO2 emergency department monitoring and critical.
Tissue hypoxia in sepsis triggers an increased respiratory rate but micro clots and hypotension impair blood flow back to the lungs to excrete. A low end-tidal CO2 may indicate poor perfusion hypovolemia or sepsis. This is a major respiratory symptom.
Savastano S et al. End-tidal carbon dioxide and defibrillation success in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest. Yamanaka MK Sue DY.
Start date May 8 2016. Previous studies have shown that low EtCO 2 levels correlate with elevated lactate levels and predict mortality in patients with suspected sepsis. The normal values are 5-6 CO2 which is equivalent to 35-45 mmHg.
On the other hand a high CO2 reading may indicate airway narrowing airway obstruction or respiratory distress. End-tidal capnography or end-tidal CO2 EtCO2 monitoring is a non-invasive technique that measures the partial pressure or maximal concentration of carbon dioxide CO2 at the end of an exhaled breath. Waveforms Those of you unfamiliar with waveform capnography may be confused by what I said in the last section.
P 005 among all prehospital variables. What does end-tidal CO2 tell you. Capnograph is an indispensable tool for monitoring metabolic and respiratory function.
Most medical sources define hypocapnia as less than 35 mm Hg for partial CO2 pressure in the arterial blood. Another term alveolar hypocapnia describes low CO2 levels in the alveoli of the lungs. Low ETCO2 levels were the strongest predictor of sepsis area under the ROC curve AUC of 099 95 CI 099-100.
Hunter CL Silvestri S Ralls R Stone A Walker A Papa L. The arterial CO2 value for normal breathing at rest is 40 mm Hg or about 53 CO2 partial pressure at sea level. It can also help the healthcare provider determine if the patient is being ventilated adequately.
Low EtCO 2 with other signs of shock indicates poor systemic perfusion which can be caused by hypovolemia sepsis or dysrhythmias.

Diagnostic Criteria For Sepsis Infection Documented Or Suspected And Download Table

Prehospital Studies Of Sepsis Download Table

Pdf Blood Transfusion Practices In Sepsis

Nclex Review Notes Heart Myocardial Infarction Nclex Air Embolism Nursing School Studying

Serum Total Carbon Dioxide As A Prognostic Factor For 28 Day Mortality In Patients With Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

Jems Using Etco2 To Detect Sepsis Youtube

Surviving Sepsis Angle Closure Glaucoma Bougie Frostbite Hot Altered Patient Central Cord Syndrome Em Quick Hits

Pin On Educational Medical Diagrams
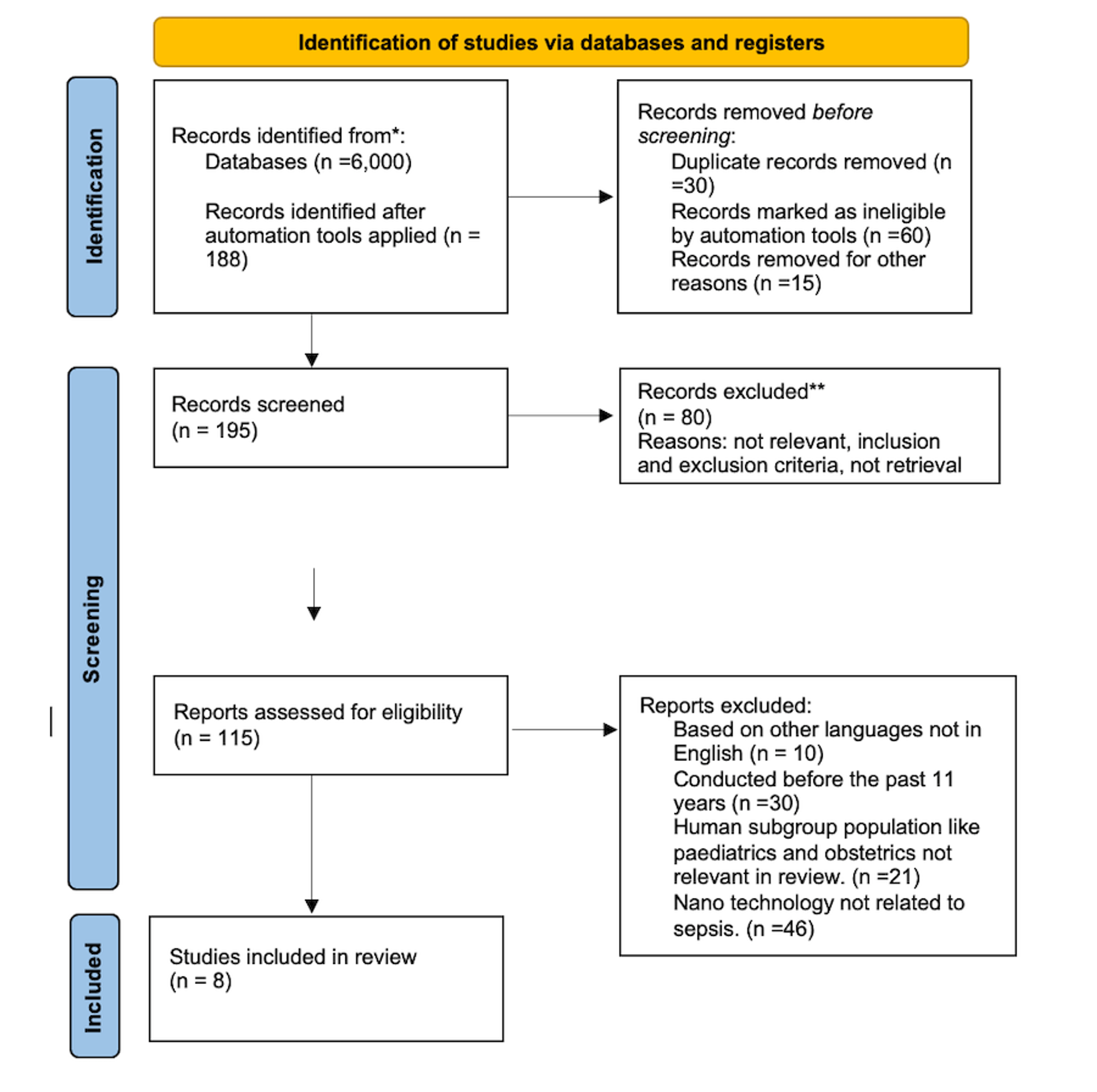
Cureus Sepsis Management Controversies And Advancement In Nanotechnology A Systematic Review
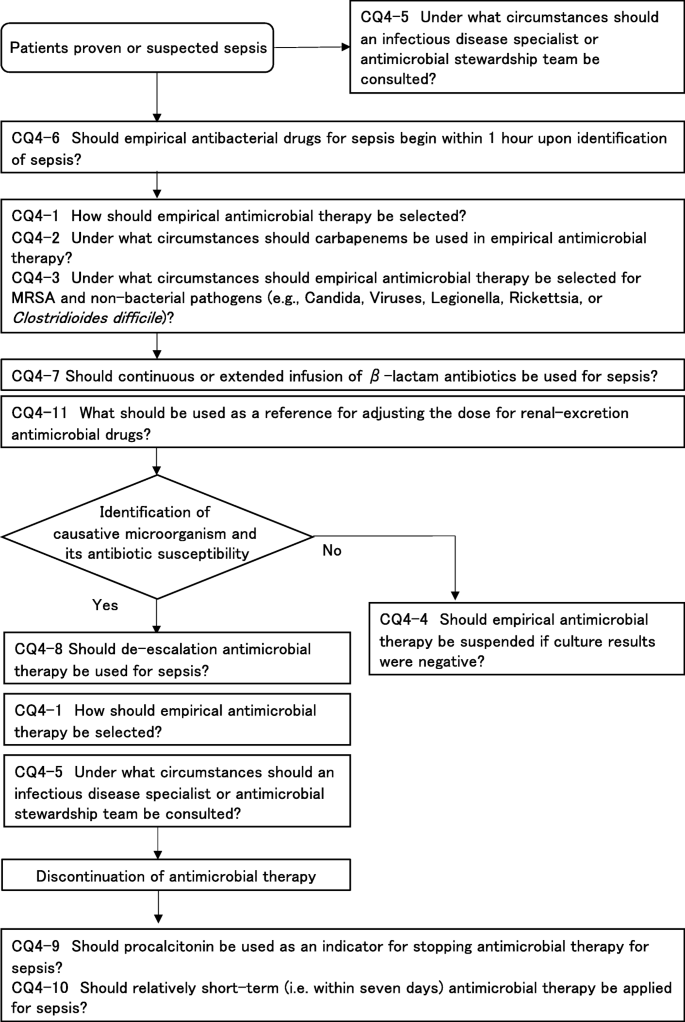
The Japanese Clinical Practice Guidelines For Management Of Sepsis And Septic Shock 2020 J Sscg 2020 Journal Of Intensive Care Full Text

Procalcitonin In Paediatric Sepsis Topic Of Research Paper In Clinical Medicine Download Scholarly Article Pdf And Read For Free On Cyberleninka Open Science Hub

Exhaled End Tidal Carbon Dioxide As A Predictor Of Lactate And Pediatric Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

6 Useful Sepsis Assessment And Treatment Tips Capnoacademy Capnoacademy

End Tidal Carbon Dioxide Is Associated With Mortality And Lactate In Patients With Suspected Sepsis The American Journal Of Emergency Medicine

How Capnography Can Be Used To Identify Sepsis

Pdf Sepsis Early Recognition And Treatment In Prehospital Setting Vital For Patient Outcomes Semantic Scholar

